DSE Dashboard
The DSE Dashboard is your starting point for any Design Space Exploration activity.
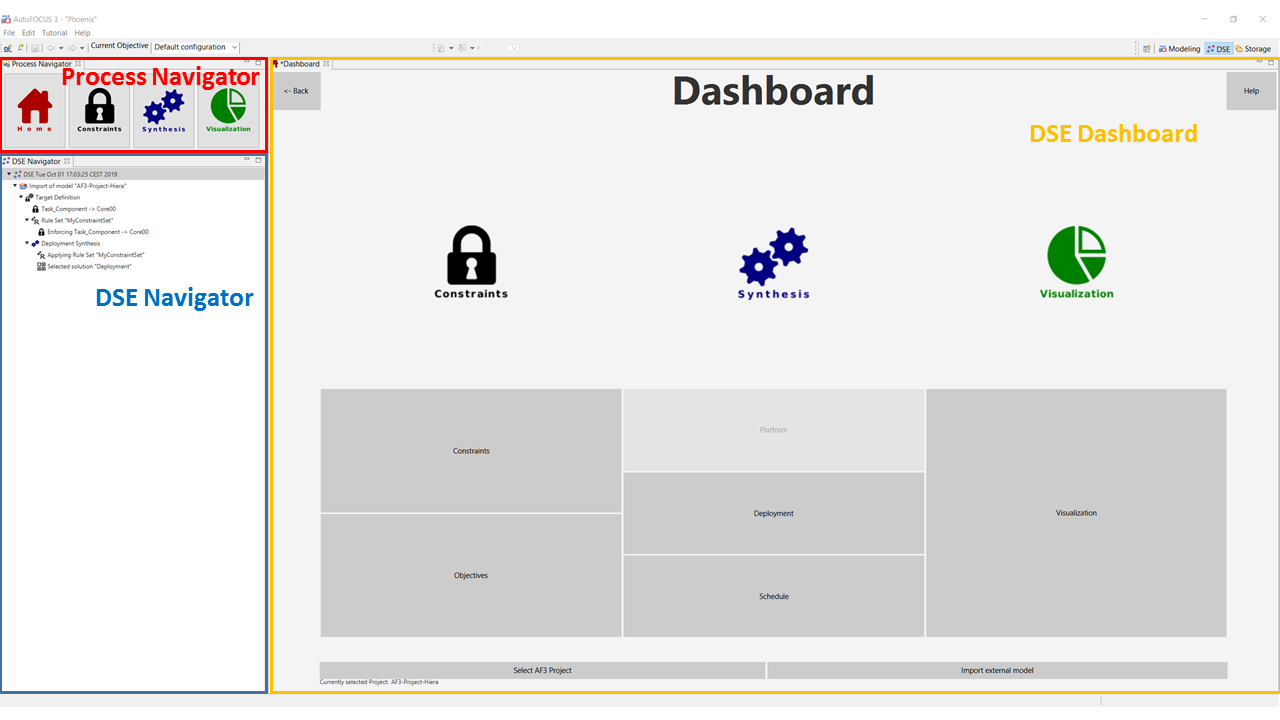
The main view (Dashboard) is divided into three columns:
- in the Constraints section (left), two buttons are provided: they allow you to access either constraints or objectives modeling;
- in the Synthesis section (centre), you can select the kind of synthesis you are interested in performing (either deployment or schedule; platform synthesis is currently not enabled);
- in the Visualization section (right), a button allows you to reach the Visualization view, in which several modalities for result visualization are provided.
In the standard perspective, on the left side, two navigators are present. These are not part of the Dashboard and will stay visible also when switching to a different view. In the top left corner you can find the Process Navigator, which will take you to any step in a DSE Process and provides a shortcut to most options available in the Dashboard. It consists of four buttons:
- the Home Button leads to the DSE Dashboard;
- the Constraints Button leads either to constraint or to objective Modeling
- the Synthesis Button leads to deployment or schedule synthesis
- the Visualization Button allows you to visualize synthesis results.
Below the Process navigator, you can find the DSE Navigator which displays in a tree-format the history of your design space exploration, i.e.:
- model imports;
- target definitions, i.e. definition of constraints and objectives;
- rule set definitions;
- synthesis performed;
- selection of artefacts returned as solution by a synthesis step.
Step 1: Importing an AF3 model or existing DSE project
Each DSE project starts with an import of an AF3 model: Therefore, press the button "Select AF3 Project" at the bottom of the Dashboard (Note: Importing external models is currently disabled). This opens a dialog where all projects present in the modelling view are listed (see figure below).

From this dialog, a new DSE project can be created from an AF3 model by selecting a top-level element from the list of projects. Alternatively, existing DSE projects can be imported. AF3 models containing a DSE project are foldable and have a black colored text whereas those without a DSE project have a gray text color.
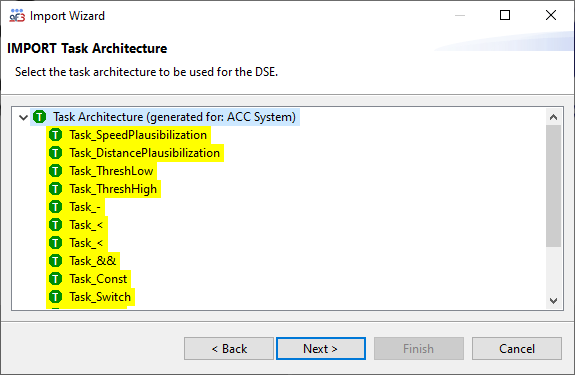
When importing a AF3 project, the wizard traverses through the model types it found in the project. It allows to select the model instance to be imported in the DSE project (see below for the import page for Task Architectures). The relevant elements for the DSE project are highlighted by a yellow background.
Step 2: Definition of Constraints and Objectives
Constraints that define the admissible solution space, or objectives that rate the quality of solutions are defined before performing the actual synthesis. The pattern-based editors to define constraints and objectives can be reached using the Constraints button of the DSE dashboard.
For the documentation of specific constraints or objectives, refer to the documentation of the respective syntheses that support them:
- Deployment Synthesis
- Allocation Constraint
- Function Coupling Constraint
- Memory Utilization Constraint
- Safety Level Constraint
- Hardware Optimization Objective
- Bus Bandwidth Optimization Objective
- Scheduling Synthesis
- Schedule Span Minimization Objective
- Energy Minimization Objective
Step 3: Execution of Design Space Exploration
In the synthesis page, the design exploration is configured and executed. First, the constraints and objectives defined in the previous steps are used to establish rule sets. Then, based on these rule sets, one of the following explorations (with or without optimization) is launched: